The 8 benefits you need to know about end-to-end encryption.

Let's decrypt together the 8 advantages of end-to-end encryption and discover why this technology has become a game changer for applications that collect sensitive data.
But before diving into the 8 benefits that end-to-end encryption offers, it's essential to understand the problem this technology can address 🧐.
Take the example of a "traditional" messaging application not encrypted end-to-end:
During the transmission of a message, the sender sends their message to the application's server, and this server then transmits it to the recipient who can read it. In this very common model, encryption is used between the sender and the server, and then between the server and the recipient (using TLS). However, the server, which acts merely as a relay, can technically read everything 👀.
Therefore, if a system administrator (who has access to the servers) were malicious or hacked, or if the application had a vulnerability allowing an attacker to take control of the server, there would be a potentially massive data breach.
The aim of end-to-end encryption is precisely to address this issue at its core by not allowing the server to read everything between senders and recipients: the message remains encrypted from one end (the sender) to the other (the recipient), without ever being decrypted between the two, hence its name 🔒.
Most messaging applications have incorporated this technology to ensure the highest level of confidentiality for messages, such as Signal, iMessage, Whatsapp, and Telegram (not by default).
Benefit 1: Increased confidentiality
End-to-end encryption is a method of securing information where only the sender and the recipient of the communication are capable of decrypting and accessing the content of the data.
In other words, the data is encrypted on the sender's device and is only decrypted once it arrives on the recipient's device.
During transit, whether on intermediary servers, networks, or any other passage point, the data remains encrypted and is therefore inaccessible to third parties, including the service providers facilitating the message's transmission.
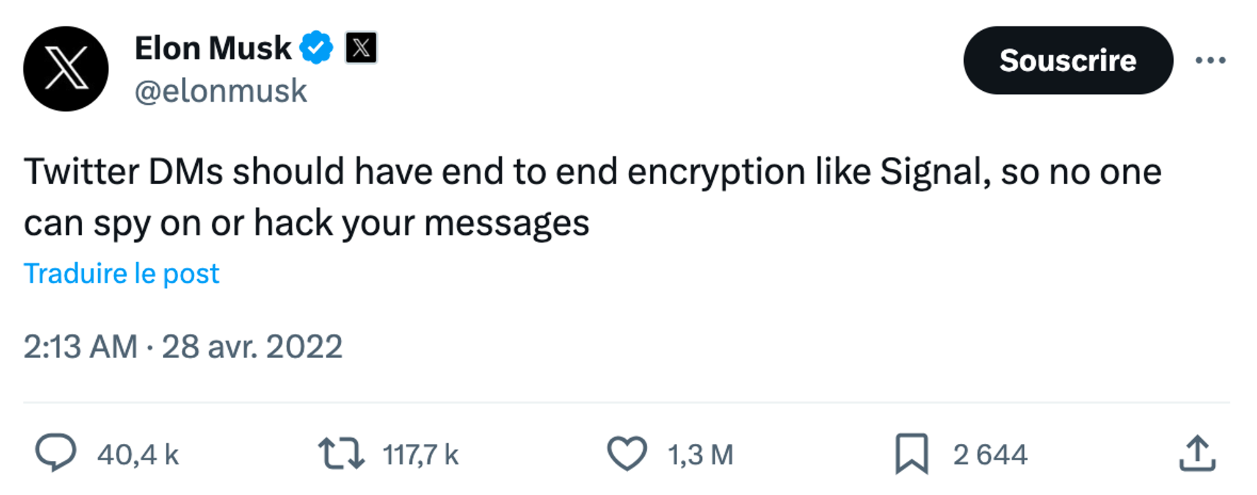
In 2022, Elon Musk discussed integrating end-to-end encryption into Twitter's messaging. He even stated: "It should be the case that I can’t look at anyone’s DMs if somebody has put a gun to my head" 😅🔫 and "Twitter DMs should have end to end encryption like Signal, so no one can spy on or hack your messages".
Benefit 2: Protection against data breach
In the event that a server containing end-to-end encrypted data is compromised, these data would remain unexploitable for the attacker.
This is likely the primary reason driving companies to adopt end-to-end encryption: to guard against data breaches. It's crucial to understand that if a malicious individual manages to breach a server containing only encrypted data, technically no data is exfiltrated as long as we can ensure the key wasn't stolen along with it. Therefore, from a GDPR perspective, it doesn't trigger a breach notification to the affected individuals. The intrusion, having had no impact, is as if nothing happened 💪.
Today, companies like Recare have implemented end-to-end encryption to ensure that only healthcare professionals can access the data (not even Recare or its hosting provider) and to prevent data theft even in the event of a breach into Recare's servers.

Benefit 3: Reduced risk of espionage
End-to-end encryption prevents malicious actors, governments, and even service providers from monitoring or accessing communications.
It might seem obvious at first glance, but if a solution can't access its users' data, it can't transmit anything to anyone. Big brother can't watch you 👀.

On this note, it's important to emphasize that the CLOUD Act, established in 2018, amends the Stored Communications Act to apply beyond U.S. borders.
As a result, U.S. courts have the authority to order American cloud providers (even if the data is stored abroad, like in France) to provide them with the entirety of an individual's data, without seeking the judicial approval of the country where the individual or data resides.
In plain terms, if data is stored on servers like AWS or GCP, the U.S. can legally access it, even if the servers are physically located in France.
Integrating end-to-end encryption into a solution using American servers would render the data on these servers inaccessible, thus avoiding any surveillance ❌.
In the EU, it's one of the supplementary security measures recommended by the European Data Protection Board for processing data in the U.S. when the Privacy Shield was invalidated.
Benefit 4: Data integrity
End-to-end encryption guarantees that the data has not been altered during transfer, as any modification of the encrypted data would render the message indecipherable.
However... beware!
We have observed a number of common errors made by developers when integrating end-to-end encryption, jeopardizing the integrity of the information 🔓.
These include the use of AES-CBC without HMAC-SHA256. If you're interested, have a look at our article: "3 common mistakes when implementing encryption".

Benefit 5: Protection against government requests
In the United States, since June 24, 2022, the Supreme Court has revoked the constitutional right of American women to abortion. This has allowed each state to define its own legislation on the subject, with some ten states (including Nebraska) banning abortion. In concrete terms, a woman who has an abortion can now be prosecuted for murder 🤬.
In 2022, in Nebraska, a girl chats with her mother on Messenger about how to end her unwanted pregnancy. At the time, there is no end-to-end encryption in Messenger.
The mother manages to obtain abortion pills by buying them on the Web and gives them to her daughter to end her unwanted pregnancy.
One police report later.... Meta (the company that develops Messenger) receives a law enforcement warrant requesting data that the platform held on the mother and her daughter. Meta had no choice but to hand over the exchanges in question.
With end-to-end encryption, Meta would not have been able to provide Messenger data to the government, as she herself would not have had the means to access the data 👌. Meta understands the importance of this technology, and has announced that Messenger will soon be end-to-end encrypted by default.

Benefit 6: Increased user trust
Knowing that your data is truly secure, thanks to end-to-end encryption, boosts users' confidence in a service or application.
In June 2020, Doctolib integrated end-to-end encryption to secure documents shared between doctors and their patients. This means that Doctolib can never access its users' sensitive information. This initiative strengthens user confidence, knowing that their medical data is shared only between themselves and their doctor. The Hippocratic oath is well-kept 👩⚕️🤫.
Benefit 7: Improved compliance
A growing number of regulations impose or recommend end-to-end encryption.
The GDPR imposes increased protection for personal data, notably through state-of-the-art encryption and minimization of stored data. According to some DPO interpretations, this constitutes an obligation to implement end-to-end encryption in certain cases ⚠️️. This requirement is therefore increasingly present in requests for proposals, particularly in the medical sector: for example in Germany for software used to manage downstream hospital beds, in Belgium for teleconsultation software and in France for teleconsultation booths.
Another example is ITAR, which applies to all U.S. military subcontractors (which covers a huge number of companies worldwide), and allows sensitive data to be used in the cloud, provided it is encrypted end-to-end (§ 120.54 (a) (5) (ii)).
Finally, NIS2, which will come into force in the second half of 2024 and apply to all critical European entities and their subcontractors, stipulates in its recital 98:
"The use of encryption, including end-to-end encryption, should if necessary be imposed on providers of public electronic communications networks or publicly available electronic communications services, in accordance with the principles of security and privacy by default and by design for the purposes of this Directive."

Benefit 8: The right to privacy
In a world where our communications can be monitored or intercepted, end-to-end encryption ensures that our confidential conversations remain truly private.
When asked about the importance of encryption, many people retort: "Why do I need it? I've got nothing to hide!"
This reaction suggests that only people hiding things or carrying out illicit activities might need encryption. Is this really the right reasoning? 🕵️♂️
Ask these same people to entrust you with their credit card codes, their online identifiers, their medical history, and you'll see that they'll suddenly grasp the value of encryption as a guarantor of their privacy.
Arguing that you don't care about privacy because you have nothing to hide is no different than saying you don't care about free speech because you have nothing to say.
